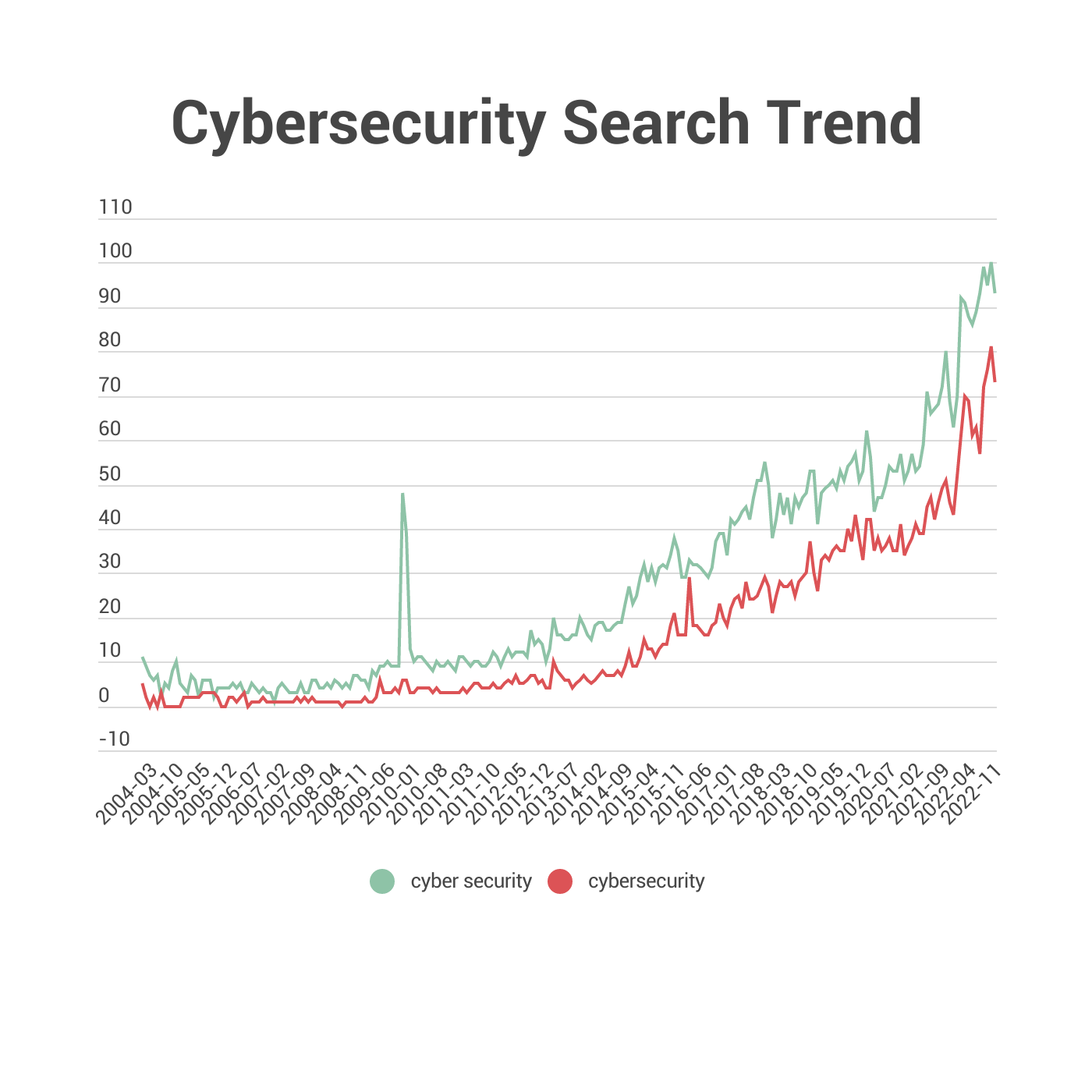
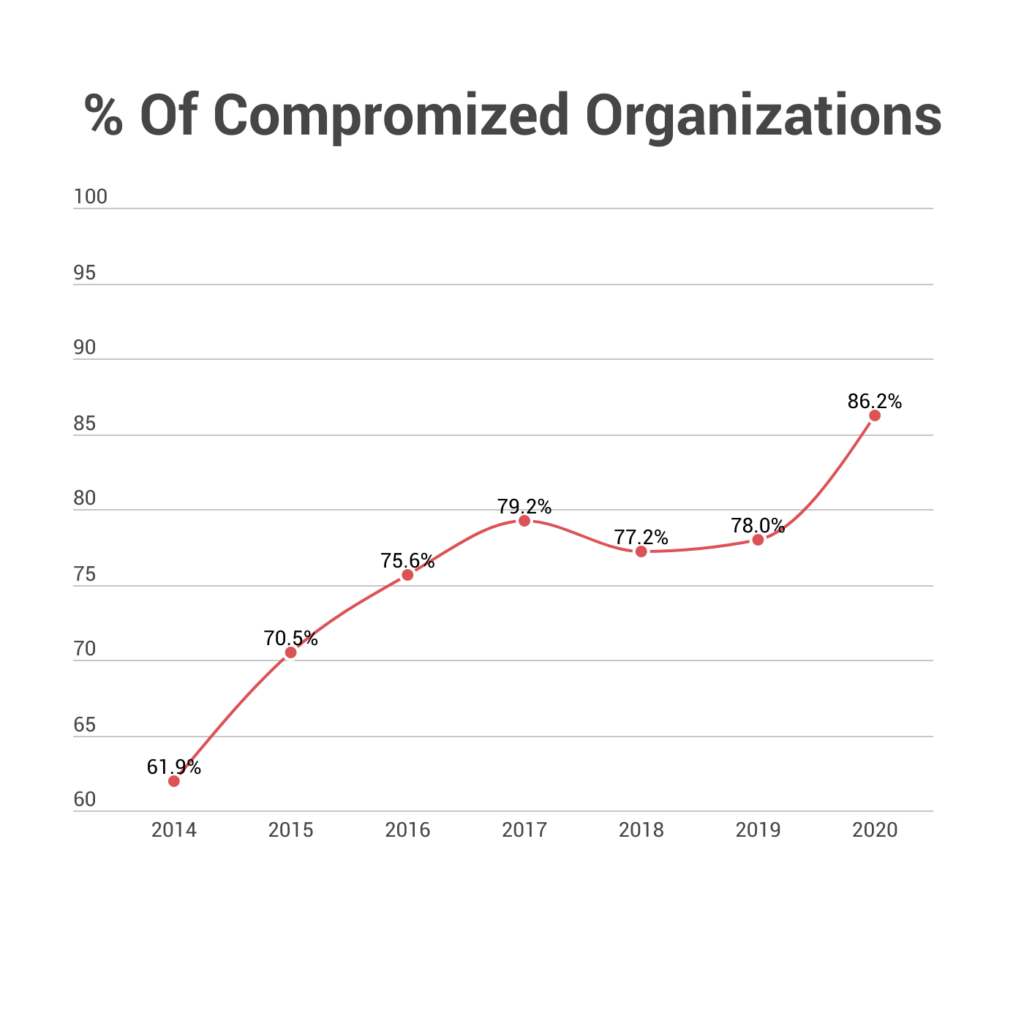
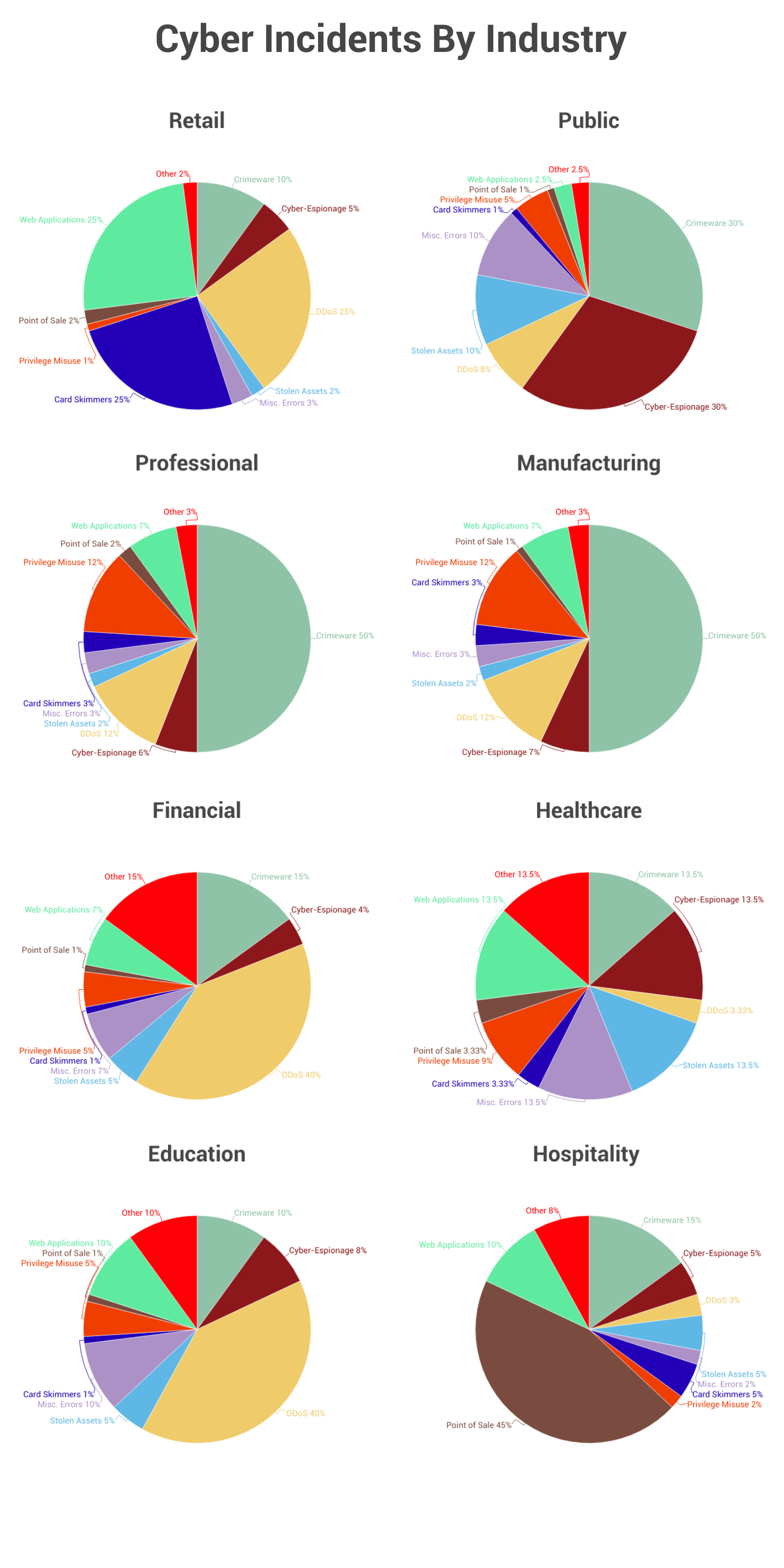
Before we dive in and learn about cyber security statistics, let’s refresh and review. What Exactly is Cyber Security ?
Cyber security is the practice of protecting computer networks and systems from unauthorized access or theft. It includes the prevention of data breaches, viruses, and other cyber attacks. Cyber security is a growing concern for businesses and individuals alike, as the number of cyber attacks continues to rise. The U.S. federal government alone has suffered over 500,000 data breaches since 2005, with over 18 million records lost or stolen in that time. These breaches can be costly, with some companies paying over $350 per record in order to reimburse their customers. As a result, almost every industry relies upon cyber security measures.
The National Institute of Standards and Technology has outlined a framework that brings structure to the field and provides useful models/rules/guidelines to follow. The standard is called the NIST Cyber Security Framework, and it is a voluntary set of standards for business and government agencies to implement to help mitigate risks to their cyber security.
It’s important to know that cyber security is not one-size-fits-all. Every business and government agency must assess their own vulnerabilities and adapt to meet their needs.
One of the questions we hear the most is, Is it Cybersecurity or Cyber Security ?
Although it seems a little confusing, it couldn’t be more simple. It all comes down to where you’re from.
American grammar coins it as Cybersecurity, which is the body of technologies, practices, and processes designed to protect computers, programs, networks and data from damage, attacks or unauthorized access. In the context of computing, the term security implies cybersecurity.
However, British grammar defines it as Cyber Security, the techniques of protecting computers , networks programs and data from unauthorized access or attacks that are aimed at exploitation.
When it comes to cyber threats, there are many to be aware of. Here are some of the most common cyber attacks and best practices on how to avoid them.
Malware: This is a type of software that is designed to damage or disable computers. It can be spread through email attachments, infected websites, or even USB drives.
Phishing: This is a type of online scam where criminals pose as legitimate businesses or individuals in order to trick people into giving them personal information or money.
Denial of Service (DoS) Attacks:This type of attack is designed to make a website or online service unavailable by flooding it with traffic from multiple computers.
SQL Injection: This is a type of attack that exploits vulnerabilities in websites or applications that use SQL databases. It can be used to steal data or take control of the database.
Password Attacks: This type of attack involves trying to guess or brute force a password in order to gain access to an account.
Cryptojacking: This is a type of malicious activity where criminals use your computer to mine cryptocurrency without your knowledge or permission.
Ransomware: This is a type of malware that encrypts your files and demands a ransom in order to decrypt them.
Social Engineering: This is a type of attack where criminals use psychological manipulation to trick people into giving them sensitive information or access to systems.
• Install and update security software. This is the first and most important line of defense against malware and other threats. Make sure you have a good antivirus program installed, and keep it up to date.
• Keep your operating system and other software up to date. Hackers often exploit security vulnerabilities that have been fixed in the latest updates. By keeping your software up to date, you can close these vulnerabilities and make it more difficult for hackers to gain access to your system.
• Use a firewall. A firewall can help to block malicious traffic and prevent hackers from gaining access to your system.
• Be cautious when opening email attachments. Email attachments are a common way for malware to spread. If you receive an email attachment from an unknown sender, or if the attachment seems suspicious, do not open it.
• Be careful what you download. Downloading files from the internet can also be a way for malware to end up on your computer. Only download files from trusted sources, and be sure to scan any downloaded files with your security software before opening them.
• Use strong passwords. Using strong, unique passwords for your online accounts can help to protect them from being hacked. Avoid using easily guessed words or phrases, and consider using a password manager to help you keep track of your passwords.