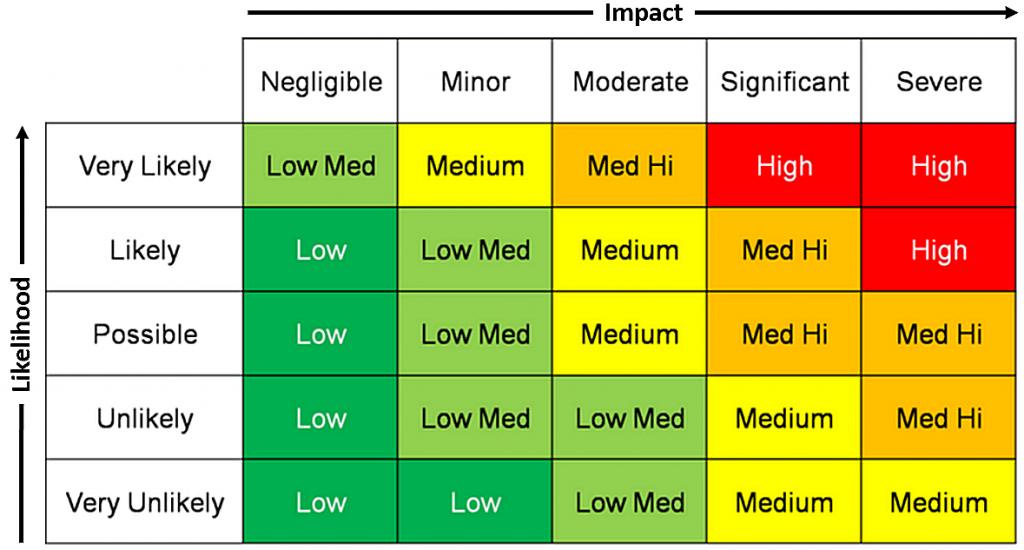
It's a common misconception that the mere presence of a hardware or software firewall guarantees an organization's infrastructure is safe from breaches. Firewalls, by their nature, permit access to public services that internet users need, such as websites, email, and DNS. In layman's terms, neglecting security measures beyond the firewall could potentially lead to calamitous outcomes in due time. Infradapt provides a thorough security assessment, comprising numerous scanning methods and policy evaluations, which culminate in a report aimed at portraying your organization's security status and suggesting enhancements.
Contact an Infradapt Solutions Specialist online or call 1-800-394-2301 to explore how Infradapt's expertise can help you mitigate IT related risk.
At Infradapt, our philosophy revolves around a proactive stance towards cyber security. It is essential for every end user who possesses, operates, or oversees information and information systems to grasp their unique security obligations fully. This understanding encompasses notions of information ownership and stewardship, as well as the part each person plays in safeguarding the information they possess, the information given to them, or any information they might encounter. We share (teach) best practices and techniques to avoid:
If you are looking for the best practical and layered approach to mitigate your Cyber Liability
and improve your Cyber Protection, Contact an Infradapt Solutions Specialist online or call 1-800-394-2301 to discoverMalware, an abbreviation for malicious software, encompasses a variety of harmful programs including spyware, ransomware, viruses, and worms. The activation of malware typically occurs when a user unsuspectingly clicks on a harmful link or attachment, resulting in the installation of detrimental software.
According to studies, once malware is engaged it can:A Denial of Service (DoS) attack is a prevalent cyber attack technique that overwhelms a computer or network, making it incapable of responding to requests. A Distributed Denial of Service (DDoS) attack operates similarly, but it originates from a computer network. Cyber attackers often employ flood attacks to interfere with the "handshake" process and execute a DoS. While other methods can be used, some cyber attackers leverage the downtime of a network to initiate further attacks.